“Did my pet gain some weight? Don’t you think your cat or dog is too overweight?”
The answers to your questions such as these are answered subjectively by us in this blog. Patient owners: “It took a little bit, but I like it that way.” “A little weight won’t do anything.” Although the answer is, excessive weight gain reduces the living standards of our pets with whom we share our lives and can even turn into an obesity disease that endangers their lives.
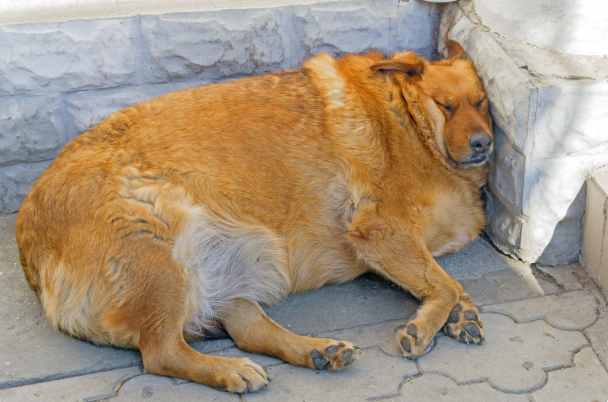

So, what is obesity that carries serious risks?
Obesity; With the excessive consumption of nutrients, pets experience metabolic, visible, etc. problems that manifest themselves as a result of excess fat. It is a common problem that can impair their functions. Carbohydrates, fats and proteins consumed in excess of requirements (aside from dry food, which is a basic nutrient in the required amount, too fatty, home-cooked food or a diet with no nutritional value is not good) are stored as fat in the animal’s body.
All our friends around us can be diagnosed with obesity, but the rate of the breeds being affected by their innate nature is increased by neutering and restricting their movements.
How do you know if our pet’s obesity regime is a problem?
The best answer at this level is; This weight gain at a certain rate is to be examined by a specialist veterinarian in order to be able to include our dog in the fat, overweight or obese categories.
Cats that are in the obese category and are checked by a veterinarian have excessive fat in the waist area, abdomen, face and lips. The extreme area of the abdomen is rounded and more swollen than normal. The bones in the ribs and other areas cannot be felt when touched/ examined by hand.
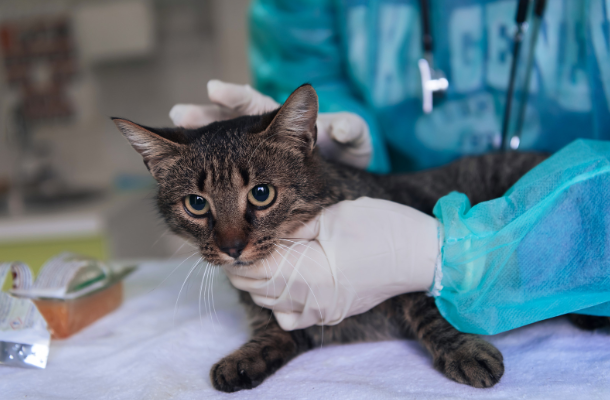

How does obesity pose a risk to the cat and its life?
Obesity; Stress on animals causes diabetes, fatty liver, increased locomotor nerves, impaired temperature regulation, risk of anesthesia, system problems, decreased reproductive efficiency, hormonal disorders and decreased lifespan.

What can be done to eliminate obesity or overweight?
Of course, it must be examined and diagnosed by a veterinarian beforehand. Then there is a significant number of cases where the owner of the patient is hiding about this issue. Scattering the parts of the animal diagnosed with obesity (e.g., walking the dog more frequently, etc.) and energy consumption are two ways that spread is achieved. However, these two processes must be maintained and checked by a veterinarian. Reducing nutrient consumption can be done in two ways. First of all, after reducing the interest rate, the digestible portion of the feed should be reduced and the water treatment of the feed should continue.
This blog post has been verified by Doctor of Veterinary Medicine Yunus Emre AŞICI.
Source:
^ a b “Obesity and overweight Fact sheet N°311”. WHO. Ocak 2015. 30 Kasım 2015 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim Tarihi: 06.10.2023
Brown RG, Dealing With Canine Obesity. Can. Vet. J. 1989. (30) 973-975. Erişim Tarihi: 06.10.2023
Butterwick RF, Hawthorne AJ. Advances in Dietary Management of Obesity in Dogs and Cats J. Nutr. December 1, 1998 vol. 128 no. 12 p:2771-2775. Erişim Tarihi: 06.10.2023
Butterwick RF, Hawthorne AJ. Advances in Dietary Management of Obesity in Dogs and Cats J. Nutr. December 1, 1998 vol. 128 no. 12 p:2771-2775. Erişim Tarihi: 06.10.2023
German AJ. The Growing Problem of Obesity in Dogs and Cats The WALTHAM International Nutritional Sciences Symposia 2006 American Society for Nutrition J.Nutr. July 2006 (136) no. 7 p:1940-1946S. Erişim Tarihi: 06.10.2023
Legrand-Defretin V. Energy Requirements of Cats and Dogs-What Goes Wrong? Int. J. Obesity 18, 1994 p:8-13. Erişim Tarihi: 06.10.2023
NRC. Nutrient Requirements of Dogs and Cats, 2011. A Technical Report Issued by the National Research Council as Part of its Animal Nutrition Series. Erişim Tarihi: 06.10.2023
NRC. Nutrient Requirements of Dogs and Cats. Your Cat’s Nutritional Needs. A Science-Based Guide for Pet Owners. National Research Council of the National Academies. 37491.Cat.P01.16.Washington, DC: National Academy Press. 2006. p: 2-13. Erişim Tarihi: 06.10.2023